해당 글은 Spring Cloud Config 로 Application의 설정 정보를 중앙에서 관리하기에 의존하는 글입니다. 실습 환경을 따라하시려면 이전 글에 나온 실습을 따라하시길 권고드립니다.
목차
- 외부 설정 관리 방법
- 기본
- 만약 설정 파일이 여러 개라면? 게다가 각각 단계별로 구성해야 하는 파일이 다르다면?
- 이럴 때 profiles 가 등장
- profiles
- Spring boot 에서 profiles 에 따른 설정
- 각기 다른 설정 정보 가져오기
- naming 전략
- config 서버 url 에 따른 설정 profile
- Config 서버와 Git Remote Repository 연동하여 설정 파일 관리하기
- Git Repository 생성
- Git 저장소 생성
- Config 서버에서 git url 연결
- User service fetch from config server
- Config Client 에서 profiles 에 따라서 다른 config 파일 불러오기
Spring Cloud Config 서버가 각기 다른 설정 파일을 가져오는 방법에 대해서 알아보기 전에 기본적으로 Spring Boot 에서 외부 설정을 어떻게 관리하고 구분하며 사용하는지 먼저 아주 간략하게 알아보도록 하자.
스프링 부트의 외부 설정 관리 방법
Spring Boot Application 에서 외부 설정에 값을 주입할 때는 잘 알다싶이 application.properties나 application.yml로 구성하곤 한다.
Spring boot application 이 빌드되고 실행될 시점에 가장 먼저 application.yml 이나 application.properties 파일을 찾고, 해당 파일에 기술된 내용을 토대로 외부 설정을 주입하게 된다.
그럼 만약 테스트 환경과 Production 환경에서 쓰일 설정을 다르게 하고싶다면 어떻게 해야할까?
예를 들어 Test 환경에서는 데이터베이스를 가볍게 돌아가는 h2 로 구성하고 싶고 Production 환경에서는 안정적인 maria db를 사용하고 싶다면?
물론 각각 설정 파일에 들어갈 설정 정보를 환경에 따라서 각기 다른 내용을 입력하면 되겠지만, 그 방법은 매우 원시적인 방법이라고 생각한다.
이런 상황에서 조금 더 우아하게 설정 정보를 교체할 수 있는 방법이 바로 Spring Profiles 라고 생각한다.
Spring Profiles 란?
Spring Profiles 란 우리의 애플리케이션의 설정을 하고 특정 환경에서만 돌아가게 하는 것을 의미한다.
보통 클래드 단으로 가서는 @Component나 @Configuration 에서 @Profiles 어노테이션을 통해 프로필을 구분하는데, 쉽게 말 해서
Spring 의 Profiles 를 이용한다면 Application 이 실행되는 환경에 따라서 다른 Bean 들을 매핑할 수 있게 된다.
현재는 Spring Cloud Config 에 대한 설명이 가장 큰 목적이니 Spring Boot 에서 Profiles 를 이용한 각기 다른 환경 구성은 Profile.active 을 이용하여 다른 설정 정보(application.properties) 불러오기 을 확인해주시기 바랍니다.
Spring Cloud Config 에서 각기 다린 설정 정보 가져오기
이제 다시 본론으로 돌아가서 Spring Cloud Config 에서는 어떻게 profiles 를 이용할까?
정답은 URL에 있다.
Spring Cloud Config 는 다음과 같은 외부 설정 파일의 3가지 정보(name, profiles, label)를 URL 경로에 따라서 구분지어놓았다.

만약 application.yml 파일이 설정 정보에 존재한다면 Global 하게 적용된다.
즉, 설정 정보를 가져가는 모든 URL에 application.yml 이 적용된다는 것이다.
예를 들어서 그럼
예를 들어서 다음과 같은 설정 파일이 존재한다고 가정해보자.
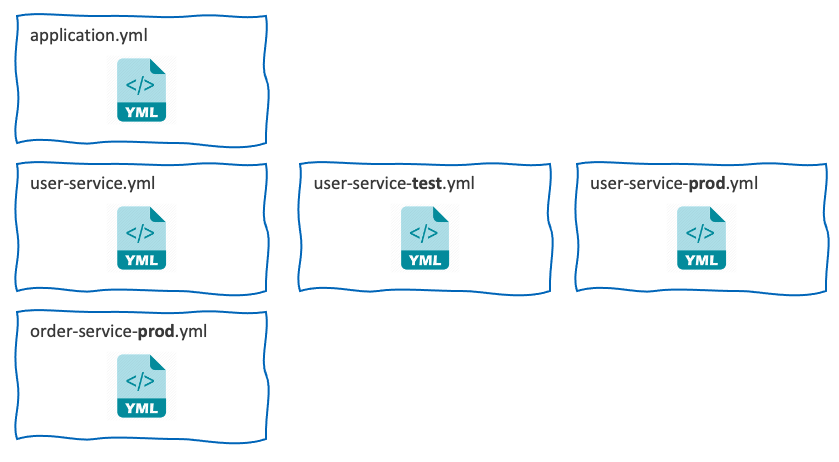
- application.yml
- user-service.yml
- user-service-test.yml
- user-service-prod.yml
- order-service-prod.yml
그럼 각각의 name과 profiles 정보로 나눌 수 있다.
- application.yml
- name: none
- profiles: none
- user-service.yml
- name: user-service
- profiles: default
- user-service-test.yml
- name: user-service
- profiles: test
- user-service-prod.yml
- name: user-service
- profiles: profiles
- order-service-prod.yml
- name: order-service
- profiles: prod
그럼 각각 어떤 url로 호출을 해야지 원하는 파일이 나올까?
사실상 위의 파일은 Config 서버에서 name이 user이 될 수도 있고 user-service가 될 수 도 있으며 user-service-test 도 될 수 있다. 이는 정하는 우리의 역량이니 우리는 user-serive 가 하나의 name이라고 가정하자
이를 구분하는 팁은 name 이 동일한 profiles는 모두 기본적으로 name.yml 파일을 갖는것이다.
즉, 위와 같은 상황은 다음과 같은 형태로 구성된다.

Config 서버와 Git Remote Repository 연동하여 설정 파일 관리하기
가볍게 Config 서버의 name과 profiles 에 대해서 알아보았으니 이제 직접 실습해보도록 하자.
지난 시간에 우리는 Config 서버를 구성하였고 Native File System에 존재하는 Local File 들을 Config 서버가 로드하여 각기 서버로 뿌려주는 것을 구현하였다.
Config Server의 기본과 설정 방법을 아신다면 무방하지만 만약 처음이시고 정확하게 실습을 따라하시고 싶다면 Spring Cloud Config 로 Application의 설정 정보를 중앙에서 관리하기 을 참고해주세요
거의 대부분의 MSA 프로젝트에서 Local 환경에 Config 파일을 관리하는 곳은 없을 것 같다.
대부분 Git을 이용해서 관리하도록 하는데, 우리도 Native File System 에서 Git 으로 설정 정보 저장소를 옮겨보자.
순서
- Git Remote Repository 생성 & Local Git 저장소 생성
- 설정 파일 추가
- Config Server 에서 Git URL 연결
- User-Service 에서 Config Server 로 부터 받은 설정 파일 이용하기
Git Remote Repository 생성 & Local Git 저장소 생성
우선 github 에 들어가서 원격 레포지토리를 생성하도록 하자.
이름은 간단하게 msa-configurations 라고 지정하겠다.

그리고 로컬 파일에서 다음과 같은 명령어로 git Local 저장소를 생성하자
mkdir git-msa-config
cd git-msa-config
git init
git remote add origin https://github.com/저장소 이름.git설정 파일 추가
그리고 각기 다른 설정 파일들을 저장하자.
- application.yml
- user-service.yml
- user-service-test.yml
# application.yml
default:
owner: config-service's git folder
content: :) 안녕하세요 각각의 마이크로서비스에서 사용될 데이터입니다. :)
# user-service.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver: com.h2.Driver
url: dbUrl
username: admin
password: admin
token:
key: my_token_secret_key
default:
message: user-service 에서 global profiles 에서 사용할 설정 정보들
# user-service-test.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: dbUrl
username: test
password: test
default:
message: test profiles 에서 사용할 설정 정보들
그리고 원격 레포지토리에 새로 생성된 파일들을 push 해보자.
git add -A
git commit -m"initial commit"
git push origin master
그럼 다음과 같이 잘 저장된 것을 확인할 수 있다.

Config Server 에서 Git URL 연결
이제 Config Server 에서 우리의 설정 정보들이 저장된 저장소와 연결을 해보자.
Config Server 에 있는 application.yml 을 다음과 같이 작성해보자.
만약 지난 시간에 실습을 따라한다면 native active profiles 이 존재할텐데, 해당 프로파일을 지워야 한다.
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: config-service
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/dhslrl321/mas-configurations
그리고 api tester 나 브라우저로 http://localhost:8888/user-service/test 로 접근한다면 다음과 같은 결과가 나올 것이다.
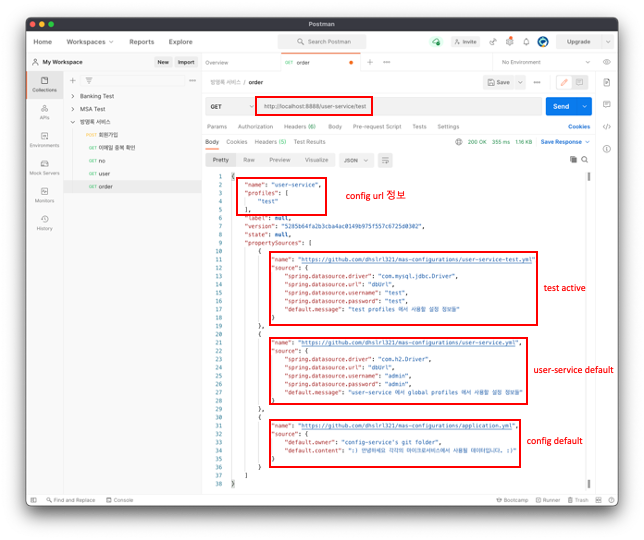
token.key는 추후에 추가한 데이터라 위의 데이터에는 token.key 정보가 없는점 양해바랍니다.
사실 민감 정보는 git private repository로 지정하는게 맞다. 더 나아가서는 암호화를 해야하는데, 이는 다음 시간에 알아보도록 하자
그럴 경우 다음과 같이 git 계정 정보를 등록할 수도 있다.
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: config-service
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/dhslrl321/mas-configurations
username: uname123
password: pwd1234Config Client 에서 profiles 에 따라서 다른 config 파일 불러오기
이제 Config Client 측, 즉 User-Service 에서 아래와 같이 controller 를 구성해서 어떤 결과가 나오는지 출력해보자.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@RestController
public class UserServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserServiceApplication.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("/config/database")
public String database(@Value("${spring.datasource.driver}") String driver,
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}") String url,
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}") String username,
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}") String password,
@Value("${token.key}") String tokenKey) {
return "driver: " + driver + "\n"
+ "url: " + url + "\n"
+ "username: " + username + "\n"
+ "password: " + password + "\n\n"
+ "token key: " + tokenKey;
}
}
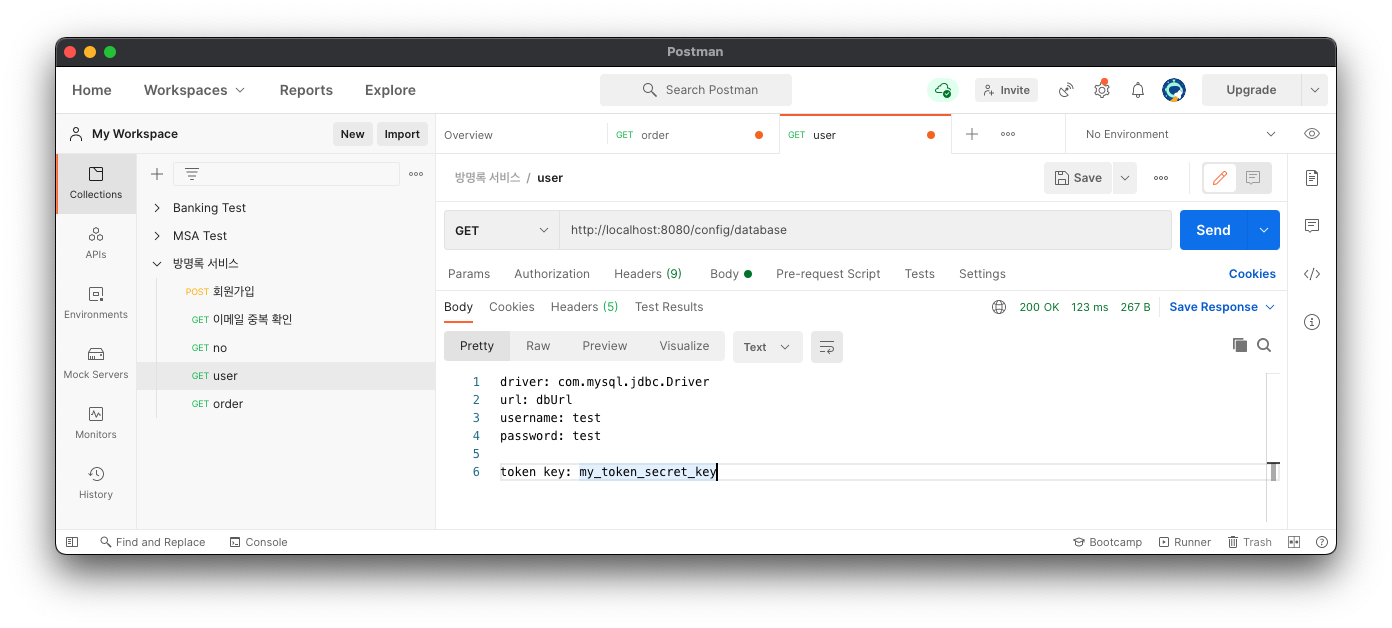
그럼 user-service에 있는 token 정보와 user-service-test 에 있는 datasource 정보를 잘 받아오는 것으로 확인된다.




댓글